CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper
CBSE
Class XI Biology
Sample Paper – 1
- Time: 3 hrs Total Marks: 70
General Instruction:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper consists of four sections A, B, C and D.
- Internal choice is given in all the sections. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Section A contains 5 questions of 1 mark each.
- Section B has 7 questions of 2 marks each.
- Section C is of 12 questions of 3 marks each.
- Section D has 3 questions of 5 marks each.
- Wherever necessary, the diagrams drawn should be neat and properly labelled.
SECTION – A
- Define cladistics.
OR
Name two botanical gardens located in India.
- What is the main function of sepals?
- Can there be mitosis without DNA replication in the ‘S’ phase?
- What does the half-leaf experiment on photosynthesis indicate?
OR
Who first showed that only the green parts of plants could release oxygen?
- What does the H-zone of a sarcomere in a myofibril contain?
SECTION – B
- What are gemmae? What role does gemma play in reproduction?
- Explain a competitive inhibitor with a suitable example.
OR
What are fatty acids? Give two examples indicating the number of carbon atoms present in each.
- What is meant by vital capacity? List any two categories of people who possess higher vital capacity.
- Where are myelinated and non-myelinated fibres commonly found in the nervous system?
- How is a key useful in the identification and classification of an organism?
- List any two points of differences between dicot stem and dicot root on the basis of their vascular bundles.
OR
Below is the diagram of lenticels. Identify the regions A, B, C and D.
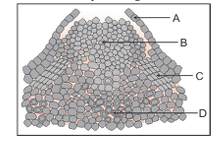
- Who proposed the double helical model of DNA? Why are two strands of DNA described as antiparallel?
SECTION – C
- What steps would you follow to classify a specimen?
- Describe the structure and functions of the tracheary elements.
OR
Understand the given description and name the cells or tissues.
- In dicotyledonous plants, it occurs in layers below the epidermis.
- Responsible for the radial conduction of water in plants.
- Central lumens are obliterated.
15.
-
- How is a pinnately compound leaf different from a palmately compound leaf?
- The transverse section of a plant material shows the following anatomical features:
- The vascular bundles are conjoint, scattered and surrounded by a sclerenchymatous bundle sheath.
- Phloem parenchyma is absent. What will you identify it as?
16. Explain with suitable examples the different types of phyllotaxy.
OR
Draw a labelled diagram of the alimentary canal of a cockroach.
17.
-
- What is meant by the dynamic state of body constituents?
- Name the form of energy which is used by living cells.
- What is an apoenzyme?
- Write any two characteristics of mitochondria and draw a labelled diagram of a mitochondrion.
- What is the significance of meiosis?
- Give one chief function and one main deficiency symptom for each of the following in plants: Iron, zinc and phosphorus.
OR
Represent diagrammatically the relationship between atmospheric, soil and biomass nitrogen pools during the nitrogen cycle.
- Where does carboxylation take place in a C3 plant? Explain the process.
- Why is the parathyroid hormone (PTH) considered a hypercalcaemic hormone?
- Name the different types of teeth and their number in an adult human.
- List any three artificial or man-made methods to overcome seed dormancy.
OR
State the name of the plant growth regulator which you will use in the following cases:
- To promote flowering in pineapples
- To stimulate early seed production in conifers
- To sprout potato tubers
- To prevent leaf drop at an early age
- To prepare weed-free lawns
- To delay leaf senescence
SECTION D
- Study the given figure of the excretory system of man carefully and answer the following questions:
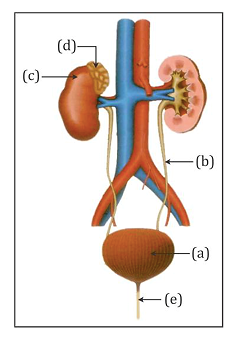
-
- Name the parts labelled (a), (b), (c), (d) and (e).
- Give one major function of each of these parts.
OR
Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each.
- Explain why
- Exogenous application of auxin fails to enhance the growth of intact plants.
- Vitamins are not considered plant growth hormones.
- It is appropriate to call a short-day plant a long-night plant.
- Some plants, belonging to halophytes and growing in marshy lands, face great difficulty in germination.
- Gibberellins do not enhance the growth of isolated plant
OR
A portion of the cross-section of leaf is shown in the diagram. Answer the following:
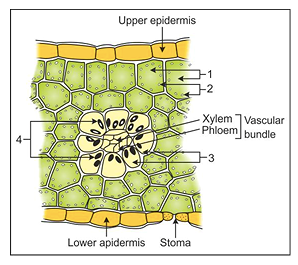
- Label 1 to 4.
- What kind of anatomy is shown in the diagram?
- Write the structure and functions of 2 and 4.
- Explain diagrammatically the mechanism of breathing and the positions of ribs, diaphragms and the thoracic cavity during inspiration and expiration.
OR
What is uraemia? Name and describe the process used to remove waste substances from individuals suffering from uraemia.


