CBSE Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Revision Notes- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1 introduces some fundamental concepts about Integers. The elementary concepts of integers are very important for students as these concepts are applied in many other chapters of Mathematics. The following notes on Integers have been prepared by our subject experts based on the NCERT textbook.
From SpeEdLabs, students can download and refer to these CBSE Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 revision Notes PDFs for free. This chapter introduces important concepts such as whole numbers, natural numbers, properties of addition and subtraction of integers, number line, etc.
Integers Class 7 Chapter 1 Notes- [Free PDF Download]
Introduction to Integers
Introduction to Numbers
Natural Numbers: The collection of all the counting numbers is called set of natural numbers. It is denoted by N = {1, 2, 3, 4….}
Whole Numbers: The collection of natural numbers along with zero is called a set of whole numbers. It is denoted by W = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5…}
Properties of Addition and Subtraction of Integers
Closure under Addition and subtraction
For every integer a and b, a+b and a–b are integers.
Commutativity Property for addition
For every integer a and b, a+b=b+a
Associativity Property for addition
For every integer a, b and c, (a+b) +c=a+ (b+c)
Additive Identity & Additive Inverse
Additive Identity
For every integer a, a+0=0+a=a here 0 is Additive Identity, since adding 0 to a number leaves it unchanged.
Example: For an integer 2, 2+0 = 0+2 = 2.
Additive inverse
For every integer a, a+ (−a) =0 Here, −a is additive inverse of a and a is the additive inverse of-a.
Example: For an integer 2, (– 2) is additive inverse and for (– 2), additive inverse is 2. [Since + 2 – 2 = 0]
Properties of Multiplication of Integers
Closure under Multiplication
For every integer a and b, a×b=Integer
Commutative Property of Multiplication
For every integer a and b, a×b=b×a
Multiplication by Zero
For every integer a, a×0=0×a=0
Multiplicative Identity
For every integer a, a×1=1×a=a. Here 1 is the multiplicative identity for integers.
Associative property of Multiplication
For every integer a, b and c, (a×b) ×c=a× (b×c)
Distributive Property of Integers
Under addition and multiplication, integers show the distributive property.
i.e., for every integer a, b and c, a× (b+c) = a×b+a×c
These properties make calculations easier.
Division of Integers
When a positive integer is divided by a positive integer, the quotient obtained is a positive integer.
Example: (+6) ÷ (+3) = +2
When a negative integer is divided by a negative integer, the quotient obtained is a positive integer.
Example: (-6) ÷ (-3) = +2
When a positive integer is divided by a negative integer or negative integer is divided by a positive integer, the quotient obtained is a negative integer.
Example: (-6) ÷ (+3) =−2 and Example: (+6) ÷ (-3) = −2
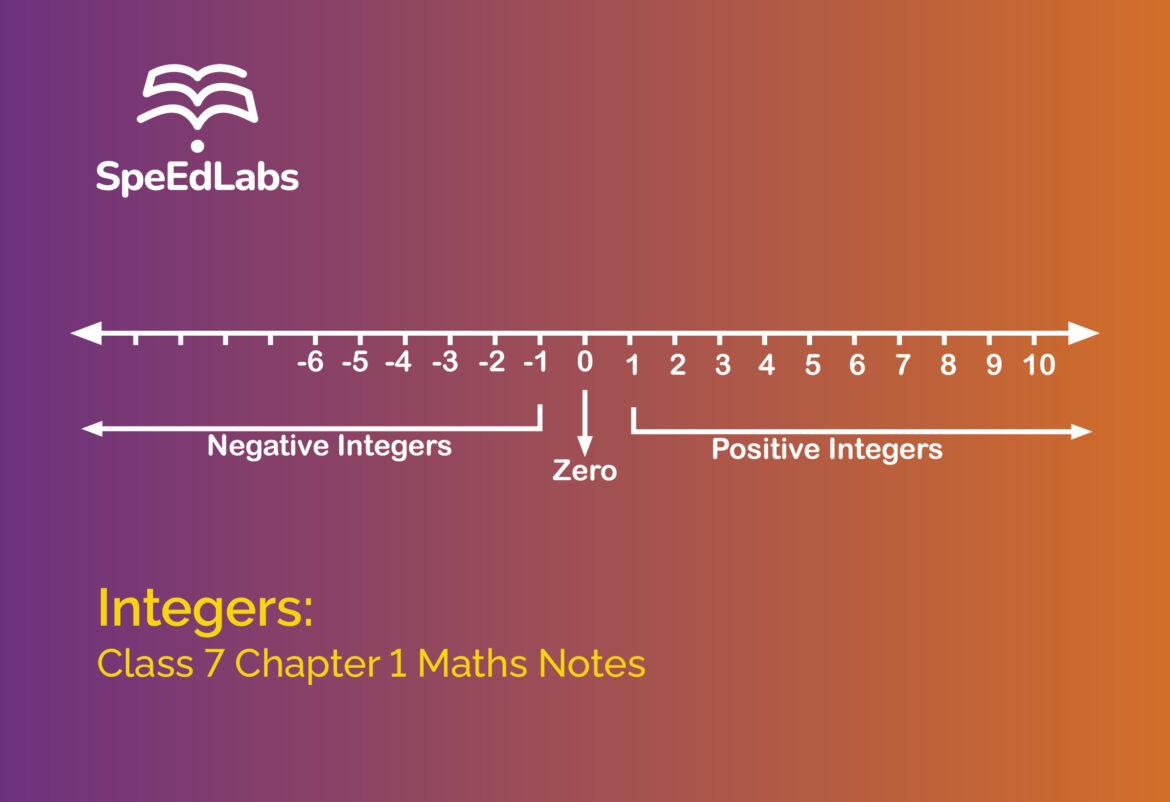
The Number Line
On a number line when we,
- Add a positive integer for a given integer, we move to the right.
Example: When we add +2 to +3, move 2 places from +3 towards right to get +5
- Add a negative integer for a given integer, we move to the left.
Example: When we add -2 to +3, move 2 places from +3 towards left to get +1
- Subtract a positive integer from a given integer, we move to the left.
Example: When we subtract +2 from -3, move 2 places from -3 towards left to get -5
- Subtract a negative integer from a given integer, we move to the right
Example: When we subtract -2 from -3, move 2 places from -3 towards right to get 1
Addition and Subtraction of Integers
The absolute value of +7 (a positive integer) is 7
The absolute value of -7 (negative integer) is 7 (its corresponding positive integer)
Addition of two positive integers gives a positive integer.
Example: (+3) + (+4) = +7
Addition of two negative integers gives a negative integer.
Example: (−3) + (−4) = −3−4=−7
When one positive and one negative integers are added, we take their difference and place the sign of the bigger integer.
Example: (−7) + (2) = −5
For subtraction, we add the additive inverse of the integer that is being subtracted, to the other integer.
Example: 56–(–73) = 56+73 = 129
Introduction to Zero
Integers
Integers are the collection of numbers which is formed by whole numbers and their negatives.
The set of Integers is denoted by Z or I. I = {…, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4…}
Properties of Division of Integers
For every integer a,
- a÷0 is not defined
- a÷1 = a
Note: Integers are not closed under division
Example: (– 9) ÷ (– 3) = 2. Result is an integer.
And (−3) ÷ (−9) = 1/3. Result is not an integer.
Multiplication of Integers
Product of two positive integers is a positive integer.
Example: (+2) × (+3) = +6
Product of two negative integers is a positive integer.
Example : ( −2) × (−3) = +6
Product of a positive and a negative integer is a negative integer.
Example: (+2) × (−3) = −6 and (−2) × (+3) = −6
Product of even number of negative integers is positive and product of odd number of negative integers is negative.
These properties make calculations easier.
Class 7 Integers Notes for Revision
The number line in Integers shows the negative values of whole numbers as well as how they are represented. By introducing negative numbers, integers expand the horizon of the definition of number line beyond natural numbers and whole numbers.
The various properties that we come across in integers such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of the integers are also useful in higher grades to understand the number system and new numbers introduced in higher grades such as rational numbers, an irrational number, etc. Thus, keeping this thing in mind, SpeEdLabs has designed Class 7 Integers notes in a manner that helps the students in quick revision before they start with the chapters introduced in the higher grade. Thus, SpeEdLabs has prepared Revision notes for Integers chapter 1 so that students can easily revise the concepts before the exams as well as in future grades.