SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER (TERM I) 2021-22
CLASS XII
BIOLOGY
Time: 90 Minutes
General Instructions:
The Question Paper contains three sections.
Section A has 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions.
Section B has 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions.
Section has 12 questions. Attempt any 10 questions.
All questions carry equal marks.
There is no negative marking.
SECTION – A
Section – A consists of 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions from this section. The first attempted 20 questions would be evaluated.
1. The structure of bilobed anther consists of
A. 2 thecae, 2 sporangia
B. 4 thecae, 4 sporangia
C. 4 thecae, 2 sporangia
D. 2 thecae, 4 sporangia
2. In the figure of anatropous ovule given below, choose the correct option for the characteristic distribution of cells within the typical embryo sac
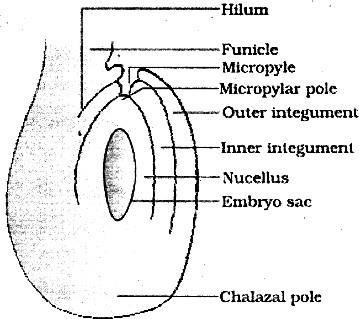
| Number of cells at chalazal end | Number of cells at micropylar end | Number of nuclei left in central cell | |
| A | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| B | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| C | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| D | 2 | 2 | 4 |
3. The coconut water from tender coconut is
A. cellular endosperm.
B. free nuclear endosperm.
C. both cellular and nuclear endosperm.
D. free nuclear embryo.
4. Pollen grains are well preserved as fossils because of presence of
A. sporopollenin
B. cellulose
C. lignocellulose
D. pectocellulose
5. Which of the following statements are true related to Seed $mathrm{X}$ and $mathrm{Y} ?$
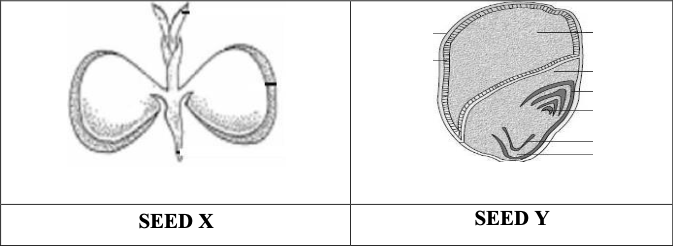
(i) Seed $mathrm{X}$ is dicot and endospermic or albuminous.
(ii) Seed $mathrm{X}$ is dicot and non-endospermic or non-albuminous.
(iii) Seed $mathrm{Y}$ is monocot and endospermic or albuminous.
(iv) Seed $mathrm{Y}$ is monocot and non-endospermic or non-albuminous.
Choose the correct option with the respect to the nature of the seed
A. (i), (iii)
B. (ii), (iii)
C. (i), (iv)
D. (ii), (iv)
6. Which of the following statements are correct with respect to hormones secreted by placenta?
(i) Placenta secretes relaxin during later stage of pregnancy.
(ii) Placenta secretes high amount of FSH during pregnancy.
(iii) Placenta secretes relaxin during initial stage of pregnancy.
(iv) Placenta secretes hCG and hPL during pregnancy.
A. (i) and (iv)
B. (i), (ii) and (iv)
C. (iii) and (iv)
D. (ii), (iii) and (iv)
7. Figure A shows the front view of the human female reproductive system and Figure B shows the development of a fertilized human egg cell
Figure A.
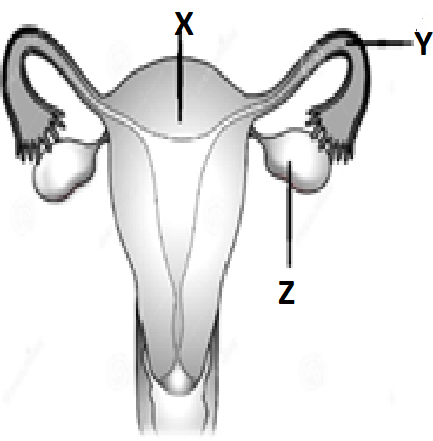
Figure B.
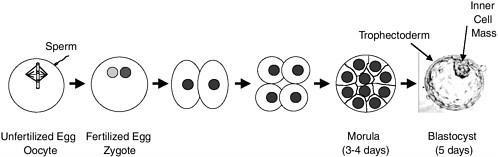
Identify the correct stage of development of human embryo (Figure B) that takes place at the site $X, Y$ and $Z$ respectively in the human female reproductive system (Figure A). Choose the correct option from the table below:
| X | Y | Z | |
| A | Morula | Fertilized egg | Blastocyst |
| B | Unfertilized egg | Fertilized egg | Morula |
| C | Blastocyst | Fertilized egg | Unfertilized egg |
| D | Fertilized egg | Morula | Blastocyst |
8. Penetration of the sperm in the ovum is followed by
A. formation of first polar body.
B. completion of meiosis II.
C. first meiosis.
D. dissolution of zona pellucida.
9. The correct sequence of hormone secretion from beginning of menstruation is
A. FSH, progesterone, estrogen.
B. estrogen, FSH, progesterone.
C. FSH, estrogen, progesterone.
D. estrogen, progesterone, FSH.
10. In the dioecious aquatic plant shown, identify the characteristics of the male flowers that reach the female flowers for pollination:
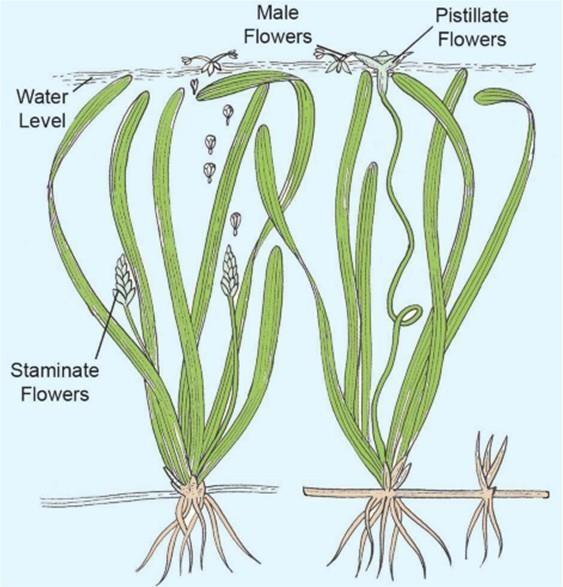
| Size of the flower | Colour of flower | Characteristic feature of pollengrain | |
| A | small | brightly coloured | Light weight and non-sticky |
| B | large | colourless | large and sticky |
| C | small | white | small, covered with mucilage |
| D | large | colourless | non sticky |
11. The thalamus contributes to the fruit formation in
A. banana.
B. orange.
C. strawberry.
D. guava.
12. How many types of gametes would be produced if the genotype of a parent is $mathrm{AaBB}$?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
13. Which of the following statements indicates parallelism in genes and chromosomes?
(i) They occur in pairs
(ii) They segregate during gamete formation
(iii) They show linkage
(iv) Independent pairs segregate independently
A. (i) and (iii)
B. (ii) and (iii)
C. (i), (ii) and (iii)
D. (i), (ii) and (iv)
14. Which of the following amino acid substitution is responsible for causing sickle cell anemia?
A. Valine is substituted by Glutamic acid in the $alpha$ globin chain at the sixth position
B. Valine is substituted by Glutamic acid in the $beta$ globin chain at seventh position
C. Glutamic acid is substituted by Valine in the $alpha$ globin chain at the sixth position
D. Glutamic acid is substituted by Valine in the $beta$ globin chain at the sixth position
15. In human beings, where genotype $mathrm{AABBCC}$ represents dark skin colour, $mathrm{aabbcc}$ represents light skin colour and $mathrm{AaBbCc}$ represents intermediate skin colour; the pattern of genetic inheritance can be termed as:
A. Pleiotropy and codominance
B. Pleiotropy and incomplete dominance
C. Polygenic and qualitative inheritance
D. Polygenic and quantitative inheritance
16. Which of the following combination of chromosome numbers represents the correct sex determination pattern in honeybees?
A. Male 32, Female 16
B. Male 16, Female 32
C. Male 31, Female 32
D. Female 32, Male 31
17. Rajesh and Mahesh have defective haemoglobin due to genetic disorders. Rajesh has too few globin molecules while Mahesh has incorrectly functioning globin molecules. Identify the disorder they are suffering from.
| Rajesh | Mahesh | |
| A. | Sickle cell anaemia – an autosome linked recessive trait | Thalassemia – an autosome linked dominant trait |
| B | Thalassemia – an autosome linked recessive blood disorder | Sickle cell anaemia – an autosome linked recessive trait |
| C. | Sickle cell anaemia – an autosome linked recessive trait | Thalassemia – an autosome linked recessive blood disorder |
| D. | Thalassemia – an autosome linked recessive blood disorder | Sickle cell anaemia – an autosome linked dominant trait |
18. Which of the following criteria must a molecule fulfil to act as a genetic material?
(i) It should not be able to generate its replica
(ii) It should chemically and structurally be stable
(iii) It should not allow slow mutation
(iv) It should be able to express itself in the form of Mendelian Characters
A. (i) and (ii)
B. (ii) and (iii)
C. (iii) and (iv)
D. (ii) and (iv)
19. The promoter site and the terminator site for transcription are located at
A. $3^{prime}$ (downstream) end and $5^{prime}$ (upstream) end, respectively of the transcription unit
B. $5^{prime}$ (upstream) end and $3^{prime}$ (downstream) end, respectively of the transcription unit
C. the $5^{prime}$ (upstream) end of the transcription unit
D. the $3^{prime}$ (downstream) end of the transcription unit
20. Which of the following is correct about mature RNA in eukaryotes?
A. Exons and introns do not appear in the mature RNA.
B. Exons appear, but introns do not appear in the mature RNA.
C. Introns appear, but exons do not appear in the mature RNA.
D. Both exons and introns appear in the mature RNA.
21. In E.coli, the lac operon gets switched on when
A. lactose is present, and it binds to the repressor.
B. repressor binds to operator.
C. RNA polymerase binds to the operator.
D. lactose is present, and it binds to RNA polymerase.
22. Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod and Maclyn McCarty used enzymes to purify biochemicals such as proteins, DNA and RNA from the heat-killed $mathrm{S}$ cells to see which ones could transform live $mathrm{R}$ cells into $mathrm{S}$ cells in Griffith’s experiment. They observed that
A. Proteases and RNases affected transformation.
B. DNase inhibited transformation.
C. Proteases and Lipases affected transformation.
D. RNases inhibited transformation.
23.
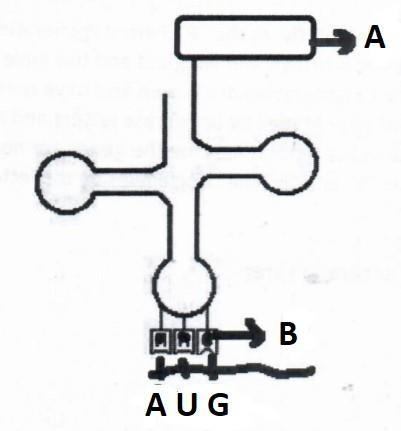
AUG on the mRNA will result in the activation of which of the following RNA having correct combination of amino acids:
| Site A | Site B | |
| A. | UAC | Methionine |
| B. | Methionine | UAC |
| C. | Methionine | AUG |
| D. | AUG | Methionine |
24. Short stretches of DNA used to identify complementary sequence in a sample are called
A. probes
B. markers
C. VNTRs
D. primers
SECTION – B
Section – B consists of 24 questions (SI. No. 25 to 48 ). Attempt any 20 questions from this section. The first attempted 20 questions would be evaluated.
Question No. 25 to 28 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both $mathrm{A}$ and $R$ are true and $R$ is the correct explanation of $A$
B. Both $mathrm{A}$ and $mathrm{R}$ are true and $mathrm{R}$ is not the correct explanation of $mathrm{A}$
C. $mathrm{A}$ is true but $mathrm{R}$ is false
D. $mathrm{A}$ is False but $mathrm{R}$ is true
25. Assertion: Lactational amenorrhea is the natural method of contraception.
Reason: It increases the phagocytosis of sperm.
26. Assertion: Saheli, an oral contraceptive for females, contains a steroidal preparation.
Reason: It is a “once a week” pill with very few side effects.
27. Assertion: Parturition is induced by a complex neuro endocrine mechanism.
Reason: At the end of gestation period, the maternal pituitary releases prolactin which causes uterine contractions.
28. Assertion: When the two genes in a dihybrid cross are situated on the same chromosome, the proportion of parental gene combinations is much higher than nonparental type.
Reason: Higher parental gene combinations can be attributed to crossing over between two genes.
29. Concentration of which of the following substances will decrease in the maternal blood as it flows from embryo to placenta through the umbilical cord?
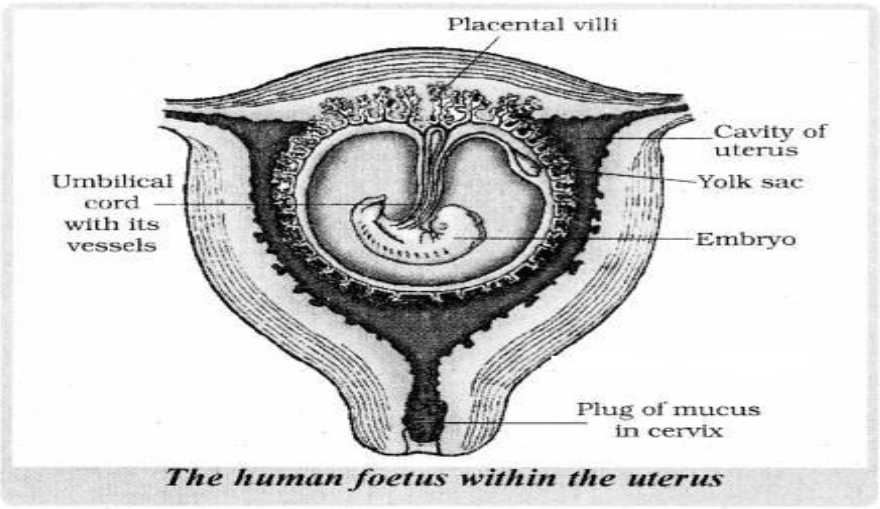
i. Oxygen
ii. Amino Acids
iii. Carbon dioxide
iv. Urea
A. i and ii
B. ii and iv
C. iii and iv
D. I and iv
30. In a fertilized ovule, $n, 2n$ and $3n$ conditions occur respectively in
A. antipodal, zygote and endosperm
B. zygote, nucellus and endosperm
C. endosperm, nucellus and zygote.
D. antipodals, synergids and integusments
31. A botanist studying Viola (common pansy) noticed that one of the two flower types withered and developed no further due to some unfavorable condition, but the other flower type on the same plant survived and it resulted in an assured seed set. Which of the following will be correct?
A. The flower type which survived is Cleistogamous and it always exhibits autogamy
B. The flower type which survived is Chasmogamous and it always exhibits geitonogamy.
C. The flower type which survived is Cleistogamous and it exhibits both autogamy and geitonogamy.
D. The flower type which survived is Chasmogamous and it never exhibits autogamy.
32. During parturition, a pregnant woman is having prolonged labour pains and child birth has to be fastened. It is advisable to administer a hormone that can
A. increase the metabolic rate.
B. release glucose in the blood.
C. stimulate the ovary.
D. activate smooth muscles.
33. A female undergoing IVF treatment has blocked fallopian tubes. The technique by which the embryo with more than 8 blastomeres will be transferred into the female for further development is
A. ZIFT
B. GIFT
C. IUT
D. Al
34. The mode of action of the copper ions in an IUD is to
A. increase the movement of sperms.
B. decrease the movement of the sperms.
C. make the uterus unsuitable for implantation.
D. make the cervix hostile to the sperms.
35. To produce $400$ seeds, the number of meiotic divisions required will be
A. $400$
B. $200$
C. $500$
D. $800$
36. A cross is made between tall pea plants having green pods and dwarf pea plants having yellow pods. In the $mathrm{F2}$ generation, out of $80$ plants how many are likely to be tallplants?
A. $15$
B. $20$
C. $45$
D. $60$
37. In Antirrhinum, $mathrm{RR} is phenotypically red flowers, $mathrm{rr} is white and $mathrm{Rr} is pink. Select the correct phenotypic ratio in $mathrm{F} 1$ generation when a cross is performed between $mathrm{RR} times mathrm{Rr}$ :
A. 1 red: 2 Pink: 1 white
B. 2 Pink: 1 white
C. 2 Red: 2 Pink
D. All Pink
38. What would be the genotype of the parents if the offspring have the phenotypes in $1: 1$ proportion?
A. $mathrm{Aa} times mathrm{Aa}$
B. $A A times A A$
C. $mathrm{Aa} times mathrm{AA}$
D. $mathrm{Aa} times mathrm{aa}$
39. What is the pa
ttern of inheritance in the above pedigree chart?
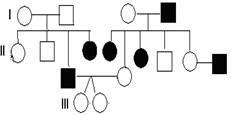
A. Autosomal dominant
B. Autosomal recessive
C. Sex-linked dominant
D. Sex-linked recessive
40. A couple has two daughters. What is the probability that the third child will also be a female?
A. $25 %$
B. $50 %$
C. $75 %$
D. $100 %$
41. Genotypic ratio of $1: 2: 1$ is obtained in a cross between
A. $mathrm{AB} times mathrm{AB}$
B. $mathrm{Ab} times mathrm{Ab}$
C. $mathrm{Ab} times mathrm{ab}$
D. $mathrm{ab} times mathrm{ab}$
42. Total number of nucleotide sequences of DNA that codes for a hormone is 1530 . The proportion of different bases in the sequence is found to be Adenine $=34 %$, Guanine $=19 %$, Cytosine $=23 %$, Thymine $=19 %$
Applying Chargaff’s rule, what conclusion can be drawn?
A. It is a double stranded circular DNA.
B. It is a single stranded DNA.
C. It is a single stranded DNA coiled on Histones.
D. It is a double stranded linear DNA.
43. A stretch of an euchromatin has 200 nucleosomes. How many bp will there be in the stretch and what would be the length of the typical euchromatin?
A. $20,000 mathrm{bp}$ and $13,000 times 10^{-9} mathrm{~m}$
B. $10,000 mathrm{bp}$ and $10,000 times 10^{-9} mathrm{~m}$
C. $40,000 mathrm{bp}$ and $13,600 times 10^{-9} mathrm{~m}$
D. $40,000 mathrm{bp}$ and $13,900 times 10^{-9} mathrm{~m}$
44. Observe structures A and B given below. Which of the following statements are correct?
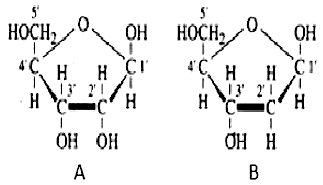
A. $mathrm{A}$ is having $2^{prime}-mathrm{OH}$ group which makes it less reactive and structurally stable, whereas $mathrm{B}$ is having $2^{prime}-mathrm{H}$ group which makes it more reactive and unstable.
B. $mathrm{A}$ is having $2^{prime}-mathrm{OH}$ group which makes it more reactive and structurally unstable, whereas $mathrm{B}$ is having $2^{prime}-mathrm{H}$ group which makes it less reactive and structurally stable.
C. $mathrm{A}$ and $mathrm{B}$ both have -mathrm{OH}$ groups which make it more reactive and structurally stable.
D. $mathrm{A}$ and $mathrm{B}$ both are having -mathrm{OH}$ groups which make it less reactive and structurally stable.
45. If Meselson and Stahl’s experiment is continued for sixth generations in bacteria, the ratio of Heavy strands ${ }^{15} mathrm{~N} /{ }^{15} mathrm{~N}:$ Hybrid ${ }^{15} mathrm{~N} /{ }^{14} mathrm{~N}:$ light ${ }^{14} mathrm{~N} /{ }^{14} mathrm{~N}$ containing DNA in the sixth generation would be
A. $1: 1: 1$
B. $0: 1: 7$
C. $0: 1: 15$
D. $0: 1: 31$
46. Two important RNA processing events lead to specialized end sequences in most human mRNAs: (i) at the $5^{prime}$ end, and (ii) at the $3^{prime}$ end. At the 5 ‘end the most distinctive specialized end nucleotide,_(iii) is added and a sequence of about 200 (iv) is added to the $3^{prime}$ end.
A. (i) Initiator codon (ii) Promotor (iii) Terminator codon (iv) Release factors
B. (i). Promotor (ii) Elongation (iii) Regulation (iv) Termination.
C. (i) Capping (ii) Polyadenylation (iii) ${ }^{mathrm{m}} mathrm{G}_{mathrm{ppP}}$ (iv) Poly $(mathrm{A})$.
D. (i) Repressor (ii) Co repressor (iii) Operon (iv) sRelease factors
47. What are minisatellites?
A. $10-40$ bp sized small sequences within the genes
B. Short coding repetitive region on the eukaryotic genome
C. Short non-coding repetitive sequence forming large portion of eukaryotic genome
D. Regions of coding strands of the DNA
48. There was a mix-up at the hospital after a fire accident in the nursery division. Which of these children belong to the parents?
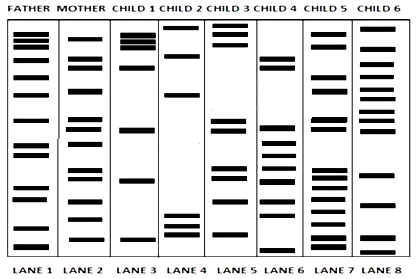
A. All of the children
B. Children $2,3 & 6$
C. Children $1 & 3$
D. Children $2 & 4$
SECTION – C
Section-C consists of one case followed by 6 questions linked to this case (Q.No. 49 to 54). Besides this, 6 more questions are given. Attempt any 10 questions in this section. The first attempted 10 questions would be evaluated
Case : To answer the questions, study the graphs below for Subject 1 and 2 showing different levels of certain hormones.
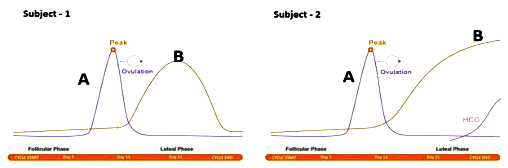
49. The peak observed in Subject 1 and 2 is due to
A. estrogen
B. progesterone
C. luteinizing hormone
D. follicle stimulating hormone
50. Subject 2 has higher level of hormone $mathrm{B}$, which is
A. estrogen
B. progesterone
C. luteinizing hormone
D. follicle stimulating hormone
51. If the peak of Hormone $mathrm{A}$ does not appear in the study for Subject 1, which of the following statement is true?
A. Peak of Hormone $mathrm{B}$ will be observed at a higher point in the graph
B. Peak of Hormone $mathrm{B}$ will be observed at a point lower than what is given in the graph
C. There will be no observed data for Hormone $mathrm{B}$
D. The graph for Hormone $mathrm{B}$ will be a sharp rise followed by a plateau
52. Which structure in the ovary will remain functional in subject 2?
A. Corpus Luteum
B. Tertiary follicle
C. Graafian follicle
D. Primary follicle
53. For subject 2 it is observed that the peak for hormone B has reached the plateau stage. After approximately how much time will the curve for hormone B descend?
A. 28 days
B. 42 days
C. 180 days
D. 280 days
54. Which of the following statements is true about the subjects?
A. Subject 1 is pregnant
B. Subject 2 is pregnant
C. Both subject 1 and 2 are pregnant
D. Both subject 1 and 2 are not pregnant
55. The gene that controls the $mathrm{ABO}$ blood group system in human beings has three alleles- $I^{A}, I^{B}$ and $mathrm{i}$. A child has blood group $mathrm{O}$. His father has blood group A and mother has blood group B. Genotypes of other off springs can be:
i. $I^{B} I^{B}$
ii. $I^{A} mathrm{i}$
iii. $I^{B} mathrm{i}$
iv. $I^{A} I^{B}$
v. $mathrm{i} mathrm{i}$
A. i, ii, iii, v
B. ii, iii, iv, v
C. iii, iv, v
D. iv, iii, i
56. Placed below is a karyotype of a human being.
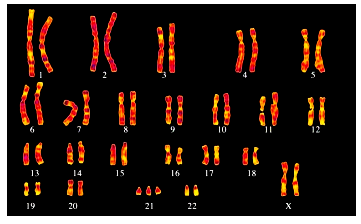
On the basis of this karyotype, which of the following conclusions can be drawn:
A. Normal human female
B. Person is suffering from Colour Blindness
C. Affected individual is a female with Down’s syndrome
D. Affected individual is a female with Turner’s syndrome
57. Given below is a dihybrid cross performed on Drosophila.
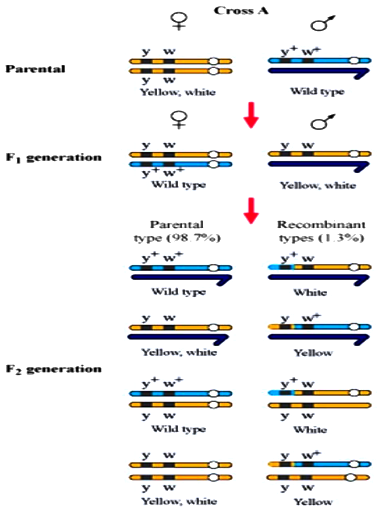
Which of the following conclusions can be drawn on the basis of this cross? When yellow bodied $mathrm{(y)}$, white eyed $mathrm{(w)}$ Drosophila females were hybridized with brown bodied $mathrm{(y+)}$, red eyed males $mathrm{(w+)}$ and $mathrm{F 1}$ progenies were intercrossed, $mathrm{F 1}$ generation would have shown the following ratio:
A. $1: 2: 1$ because of linkage of genes
B. $9: 3: 3: 1$ because of recombination of genes
C. Deviation from $9: 3: 3: 1$ ratio because of segregation of genes
D. Deviation from $9: 3: 3: 1$ ratio because of linkage of genes
58. Which cellular process is shown below?
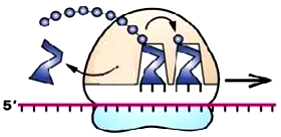
A. DNA Replication
B. Translation – Initiation
C. Translation – Elongation
D. Translation – Termination
59. Origin of replication of DNA in $E$. coli is shown below, Identify the labelled parts (i),(ii), (iii) and (iv)
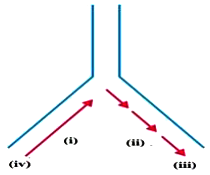
A. (i)- discontinuous synthesis, (ii)- continuous synthesis (iii) $3^{prime}$ end (iv) $5^{prime}$ end
B. (i)- continuous synthesis, (ii)- discontinuous synthesis (iii) $5^{prime}$ end (iv) $3^{prime}$ end
C. (i)- discontinuous synthesis, (ii)- continuous synthesis (iii) $5^{prime}$ end (iv) $3^{prime}$ end
D. (i)- continuous synthesis, (ii)- discontinuous synthesis (iii) $3^{prime}$ end (iv) $5^{prime}$ end
60. Transcription unit is represented in the diagram given below.
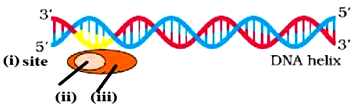
Identify site (i), factor (ii) and Enzyme (iii) responsible for carrying out the process.
A. (i) Promoter Site, (ii) Rho factor (iii) RNA polymerase
B. (i) Terminator Site, (ii) Sigma factor (iii) RNA polymerase
C. (i) Promoter Site, (ii) Sigma factor (iii) RNA polymerase
D. (i) Promoter Site, (ii) Sigma factor (iii) DNA polymerase
